
Faster
Cheaper
Smarter
Product Cybersecurity Made Simple

Trusted by market leaders
Customers that we have provided services to
One solution to comply with all

Regulation (EU) 2023/1230
Machinery Regulation
Implement new cybersecurity measures required by the Machinery Regulation.

Regulation (EU) 2017/745
Medical Device Regulation
Integrate cybersecurity into design controls for seamless Medical Device Regulation audits.

via General Safety Reg (EU) 2019/2144
UNECE R155 / R156
Achieve and maintain UNECE automotive compliance with proven systems.

Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/30
Radio Equipment Directive
Define practical processes for full Radio Equipment Directive compliance.

Regulation (EU) 2024/2847
Cyber Resilience Act
Operationalize the Cyber Resilience Act into your quality system today.
Compliance in 60 seconds
Watch the 60-second introduction.
Product categories in scope

Industry
Automotive
Structure complex development and meet UNECE compliance efficiently.

Industry
Industrial
Secure connected products without slowing speed or innovation.

Industry
Machinery
Practical cybersecurity that naturally fits your existing development process.

Industry
Control Units
Frameworks to seamlessly integrate protection into ECU development.

Industry
Radio Emission
Translate complex RED 3.3 rules into actionable engineering design.

Industry
Medical Devices
Achieve security, compliance, and faster time-to-market.
Professional automation tools
quma.
ai
Top features:
What we do for you
Turnkey Solutions

Custom Integrations
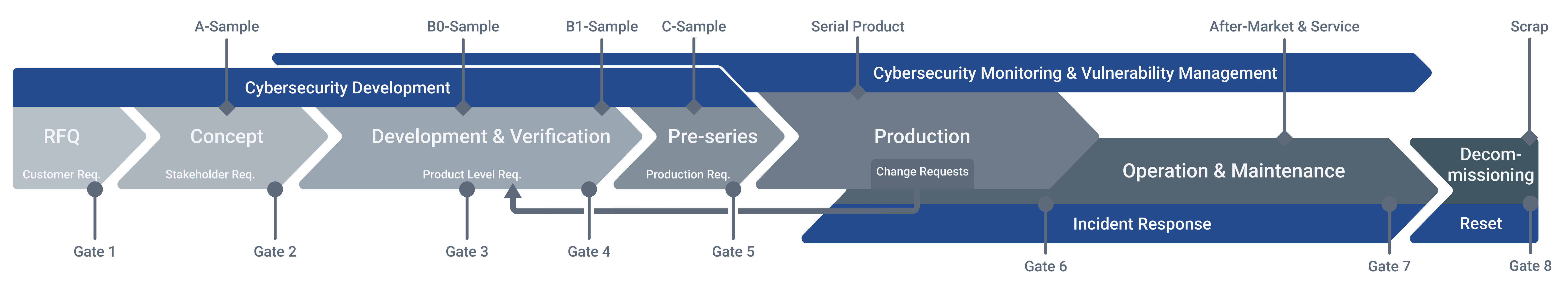

Implementation
Process Design
From plan to practice. Tailored processes for seamless cybersecurity operations.

Strategy
Department Setup
Build to last. Launch an audit-ready, effective cybersecurity department.

Strategy
Process Analysis
Know your gaps. Get the roadmap to bulletproof cybersecurity compliance.

Implementation
Software Integration
Connect everything. Integrate tools for lightning-fast, smarter cybersecurity workflows.

Strategy
Automation Strategy
Work smarter. Automate cybersecurity for faster, cheaper, better protection.

Implementation
Moderation & Audits
Audit confidence. Expert training and guidance for effortless success.
What can we do for you?
What we get asked a lot
The most common questions about us.
Do you provide a turnkey solutions for cybersecurity?
Can quma.ai integrate into our existig process?
Do your mean 10x Faster, Cheaper and Smarter literal?
Can AI already replace cybersecurity engineers ?
How long does it take to setup your turnkey solution?















